Synthesis of Protoporphyrin-Lipids and their Liposome Formation
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a tumor treatment modality that uses a combination of photosensitizer, oxygen, and tissue-penetrating light. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated from molecular oxygen through energy transfer of the photosensitizer induce significant oxidative damage to biomolecules, and cell death occurred as a result (Figure 1). The selective accumulation of the photosensitizer in tissue and the subsequent light-irradiation dose applied to the target tissue are important issues for the successful application of PDT. Various classes of photosensitizers have been designed and synthesized so far, including porphyrins, phthalocyanines, chlorins, and non-porphyrin dyes. However, most photosensitizers tend to be poor soluble in water. Therefore, much attention has been focused on drug-delivery vehicles as nanoscale drug-delivery platforms, such as liposomes.
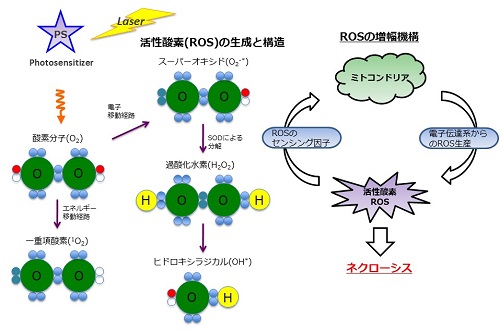 Figure 1. Concept of photodynamic therapy
Figure 1. Concept of photodynamic therapy
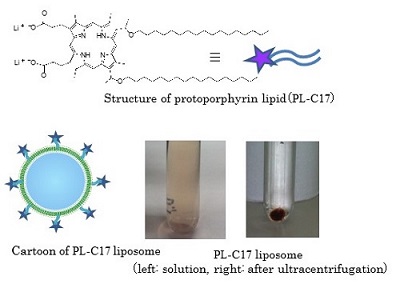
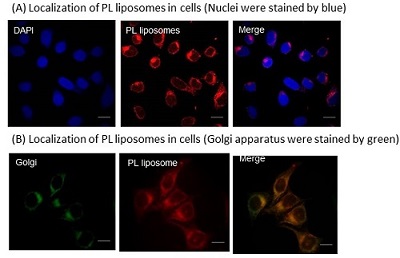
We are interested in the development of a water-soluble PPIX. To this end, we focused on the structure of PPIX and designed PPIX lipid (PL-C17) by introducing a long alkyl chain to each vinyl group on PPIX via hydrobromination, in hopes that PL-C17 would form micelles in water. We developed an alternative strategy for the liposomal delivery of photosensitizers, which involved the post-insertion of PL-C17 into liposomal bilayer (Figure 2)
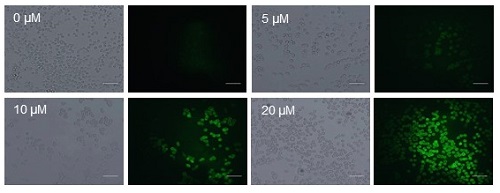
The antitumor effect of PL-C17 liposomes on HeLa cells under light irradiation was examined. HeLa cells were incubated for 3 h in medium containing various concentrations of PL-C17 liposomes. Then, the cells were irradiated with a xenon lamp (88mW/cm2, average) in the 400 to 800 nm range for 2 min. After incubation for 72 h, cell viability was determined by the MTT assay. Significant cell growth inhibition was observed by the PL-C17 liposomes with IC50 of 12.9 µM. ROS production is crucial for efficient PDT. Therefore, ROS generation by PL-C17 liposomes in cells under light irradiation was examined. Figure 4 shows the ROS generation after light irradiation for 2 min in the presence of PL-C17 liposomes at 0-20 µM concentrations. PL-C17 liposomes effectively induced ROS generation in HeLa cells under light irradiation, resulting in the significant PDT effect.


 日本語
日本語